What is the Circular Economy?
Our current economy is predominantly based on a linear process, where we take materials from the Earth, turn them into products, and then throw them away as waste at the end of their life.
Circular economy is a model of production and consumption that focusses on designing products that are more durable, reusable, repairable and recyclable to extend their lifetime and reduce waste.
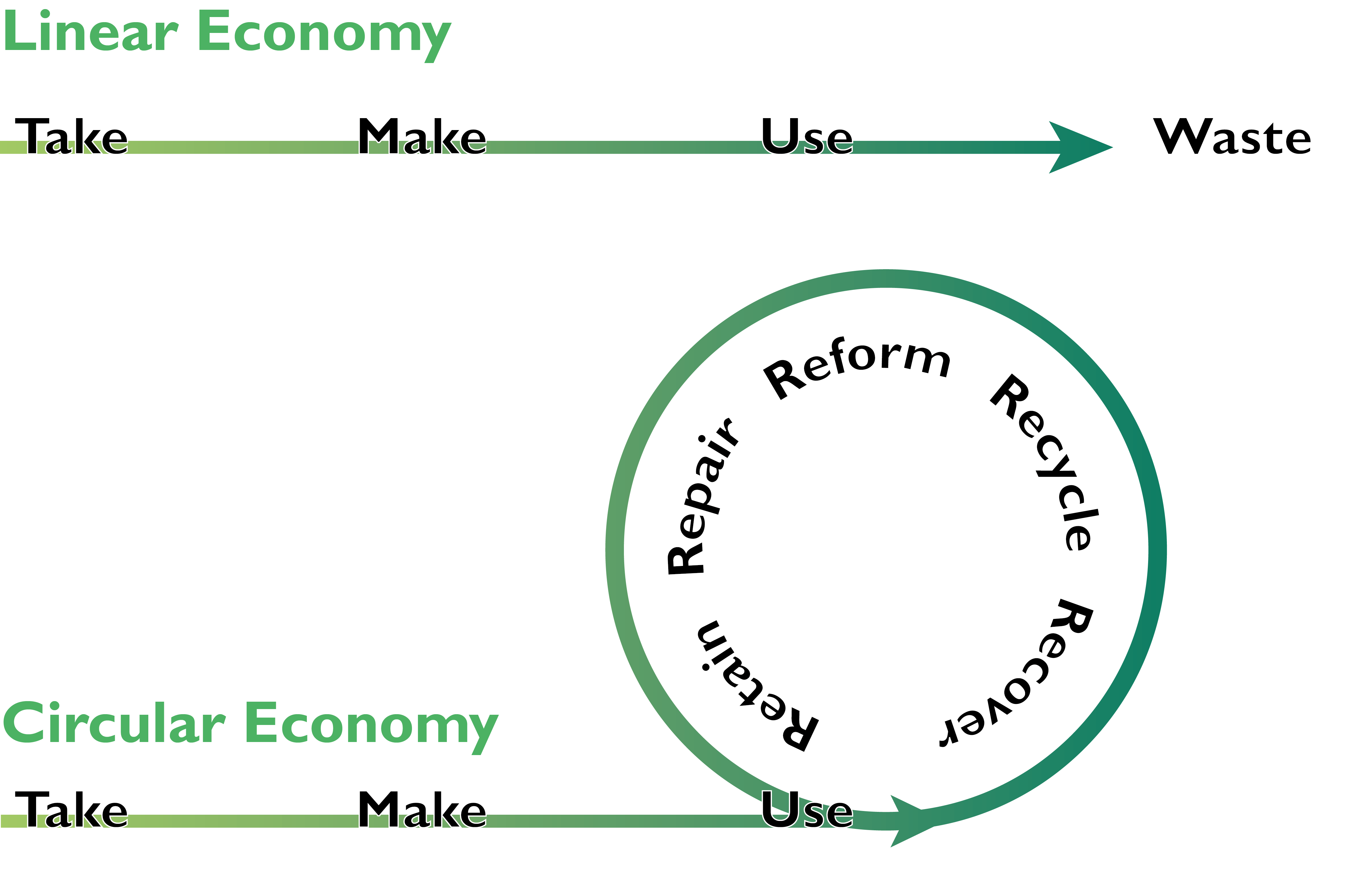
Why do we need to transition to a circular economy?
Supplies of raw materials are finite and becoming increasingly expensive, so if we are to continue to meet the needs of the growing global population, we need to make better use of products. A linear economy also uses a large amount of energy, and contributes to a large amount of waste and pollution, which puts significant pressure on the environment.
What are the benefits of a circular economy?
Moving to a circular economy would alleviate pressure on the environment and improve the security of raw materials. Not only does recycling materials use less energy than creating new products, consumers benefit from more durable products that save them money in the long run. A circular economy is also associated with economic benefits, as it can stimulate innovation and create new jobs.
How can we move from a linear to a circular economy?
The transition to a circular economy will depend on smart materials design so that products last longer and are easier to repair and recycle. It will also require a cultural change, and new models of business and trade that consider the entire product lifecycle.
How will ReMade@ARI contribute to a circular economy?
The ReMade project is committed to supporting the development of innovative, sustainable materials by providing scientists with analytical tools to explore the properties and structure of materials right down to atomic resolution.
How does ReMade@ARI relate to the European Circular Economy Action Plan (CEAP)?
Supporting the ReMade@ARI project is one of the initiatives undertaken by the European Commission, to influence how future products are designed, to promote circular economy processes, and to ensure that waste is prevented and the resources used are kept in the EU economy for as long as possible.
Read more about the EC’s CEAP.
